🔍 Introduction
Bakta is a powerful tool for the rapid and standardized annotation of bacterial genomes, MAGs and plasmids, from both isolates and metagenome-assembled genomes (MAGs).
It provides dbxref-rich, sORF-inclusive, taxon-independent annotations in machine-readable formats such as JSON, GFF3, GenBank, EMBL, TSV, and FASTA, ensuring compatibility with downstream workflows.
Unlike protein-only functional annotators (e.g., EggNOG-mapper), Bakta is a full annotation pipeline, comparable to Prokka, DFAST, and PGAP, capable of:
- Predicting CDS (coding DNA sequences) and non-coding RNAs (tRNA, rRNA, tmRNA, ncRNA)
- Detecting CRISPR arrays and origins of replication (oriC/V)
- Adding functional descriptions and stable cross-references to major databases (RefSeq, UniRef100, UniParc), facilitating FAIR-compliant and reproducible analyses.
This makes Bakta a complete solution for researchers working with bacterial genome annotation, comparative genomics, and downstream bioinformatics pipelines.
🧰 Prerequisites
- Access to Constellab and a valid Digital Lab environment
- Installed bricks:
gws_ubiome version ≥ 0.13.6 - Input file:
A genome assembly in FASTA format (contigs, plasmids, MAGs)
Bakta Database:
A pre-downloaded Bakta DB (
db-full, db-light, or db) generated using Build/Update Bakta Databasetask.
🧪 Use Case Steps
- Import your genome FASTA into Constellab.
- Link it to the Task:
"Procaryotes Genome Annotation".
- Configure Parameters:
prefix: Output prefix (default: FASTA stem).
genus, species, strain: (optional) Organism metadata.
translation_table: Choose genetic code (default: The Bacterial, Archaeal and Plant Plastid Code, NCBI 11).
replicon_type & replicon_topology: Apply to all contigs if desired (e.g., plasmid + circular).
complete_genome: Mark sequences as complete (optional).
threads: Number of CPU threads to allocate.
- Run the Task:
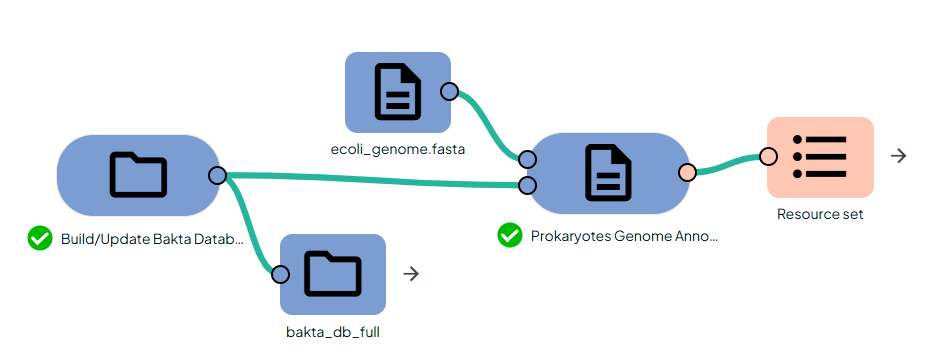
📂 Output
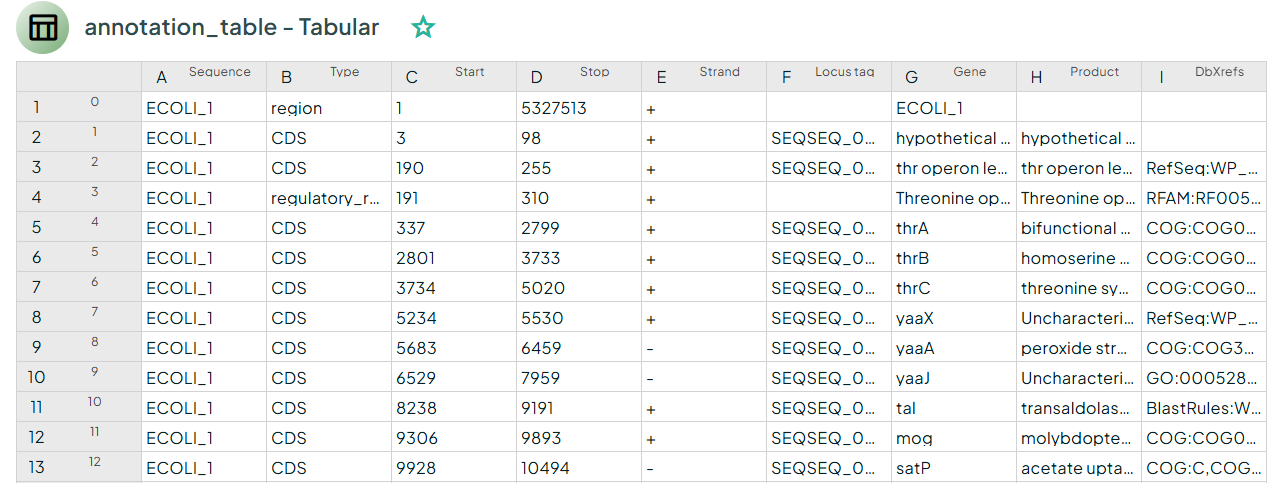
Bakta produces a set of standardized files for downstream use:
✅ Example Use Cases
- Annotating new bacterial isolates before submission to NCBI/ENA.
- Adding functional context to MAGs in metagenomic studies.
- Comparing plasmid vs chromosome content.
- Generating publication-ready genome maps.
🧬 Comparative Summary: Bakta vs eggNOG-mapper

